Main-group metal cyclophane complexes with high coordination numbers†
Abstract
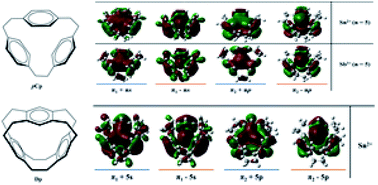
Density functional theory calculations using the PBE0-D3BJ hybrid functional have been employed to investigate the complexation of main-group metal-cations with [2.2.2]paracyclophane and deltaphane. Geometry optimization under symmetry constraints was performed to observe the mode of coordination that a metal-cation adopts when it resides inside the cyclophane cavity. Thermodynamic properties were investigated to note the trends of stability along a group of metals. To further investigate the bonding properties, Morokuma–Ziegler energy decomposition analysis, natural bond orbital analysis and Bader's analysis were employed. It was observed that most of the main-group metal complexes with cyclophanes prefer an η6η6η6 coordination mode where the metal-cation sits in the centre of the cyclophane cavity. There is an increased thermodynamic stability in [2.2.2]paracyclophane complexes compared to their deltaphane analogues while the reverse is true regarding the strength of coordination based on interaction energy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...