Comparison of the oxidation of halogenated phenols in UV/PDS and UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation processes†
Abstract
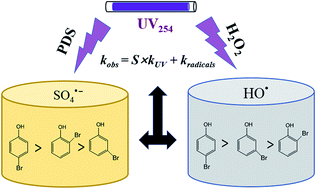
UV/peroxydisulfate (PDS) and UV/hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) can effectively degrade halophenols (HPs, e.g., 2,4-bromophenol and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol); meanwhile, information about the discrepancies in the related degradation kinetics and mechanisms of these two processes is limited. To gain this knowledge, the degradation of two typical HPs (i.e., bromophenols and chlorophenols) in UV/PDS and UV/H2O2 processes were investigated and compared. The results showed that the degradation rates of HPs with different substitution positions in the UV/PDS process were in the order of para-substituted HPs (i.e., 4-BP and 4-CP) > ortho-substituted HPs (i.e., 2-BP and 2-CP) > meta-substituted HPs (i.e., 3-BP and 3-CP), while in the UV/H2O2 process, these rates were in the order of para-substituted HPs > meta-substituted HPs > ortho-substituted HPs. These discrepancies were ascribed to the different reaction activities of SO4˙− and HO˙ with HPs, which were calculated based on the competition method. Further density functional theory (DFT) calculations suggested that SO4˙− reacts more readily with HPs via electron transfer than HO˙. In the presence of water matrices (such as Cl−, HCO3− and natural organic matter (NOM)), the degradation of 2-BP in both UV/PDS and UV/H2O2 treatment processes was inhibited due to the scavenging of free radicals by these background substances. The degradation products and pathways further confirmed that SO4˙− is a strong one-electron oxidant that reacts with HPs mainly via electron transfer, while HO˙ reacts with HPs via electron transfer and hydroxyl addition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...