The development of isoguanosine: from discovery, synthesis, and modification to supramolecular structures and potential applications
Abstract
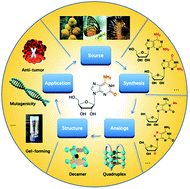
Isoguanosine (isoG), an isomer of guanosine (G), differs from G by the translocation of the C2 carbonyl and C6 amino groups. This minor translocation of functional groups results in significant differences in the properties of G and isoG. Like G, isoG can self-assemble into various supramolecular structures such as tetramers and decamers in the presence of various cations. And it shows a wide range of applications including in ionophores, genetics, gel formation, and cancer treatment. Although there have been many studies and reviews concerning G in recent years, to the best of our knowledge, there have been no reviews that summarized isoG works. Herein, the discovery, synthesis, modification, supramolecular structures and potential applications of isoG are systematically reviewed in this article, in order to provide a reference for future studies.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 Reviews in RSC Advances


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...