Identification of H2S/NO-donating artemisinin derivatives as potential antileukemic agents†
Abstract
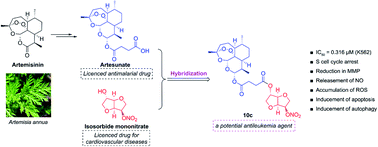
Three H2S/NO-donating artemisinin derivatives were designed and synthesized. Their antiproliferative activities were evaluated against human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell lines of K562 and K562/ADR and human normal liver cells of LO2. Biological evaluation indicated that NO-donating compound 10c exhibited the most potent cytotoxicity against leukemia cells, similar to the bioactivity of clinical drug of homoharringtonine, but showed less toxicity than homoharringtonine against LO2 cells. Further mechanism studies revealed that 10c could enhance the levels of intracellular NO and ROS, induce apoptosis and S phase cell cycle arrest, and disturb the mitochondrial membrane potential in K562 and K562/ADR cells. Western blot results demonstrated that 10c noticeably promoted autophagy by up-regulating the levels of Beclin1 and L3-II expression, inhibited the AKT signaling, and stimulated the AMPK and JNK signaling in both leukemia cell lines. Overall, 10c exhibited the potential to be a promising candidate for the therapy of AML.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...