Effect of different pyrolysis temperatures on physico-chemical characteristics and lead(ii) removal of biochar derived from chicken manure†
Abstract
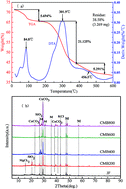
Biochar derived from chicken manure, as an effective metal adsorbent, was prepared through a pyrolysis method at different pyrolytic temperatures (200, 400, 600, and 800 °C). The physicochemical characteristics of chicken manure biochar (CMB) and its lead (Pb2+) adsorption mechanisms were studied by batch adsorption experiments, DTA/TGA, XRD, SEM-EDS, FTIR and an analysis of the composition of their mineral ash. Results showed that the best-fit for the Pb2+ adsorption data was achieved using a Langmuir isotherm and a pseudo-second-order model. The maximum adsorption capacities of Pb2+ increased with increasing of pyrolytic temperatures of the CMB, being 180.21, 200.80, 239.59, and 242.57 mg g−1, respectively, for CMB-200, CMB-400, CMB-600 and CMB-200. Although Pb2+ adsorption on CMB revealed that adsorption was controlled by multiple mechanisms, (e.g. surface complexation, ion exchange, surface precipitation, electrostatic attraction, physical adsorption, and co-precipitation), the ion exchange and surface precipitation played a dominant role in Pb2+ sorption. Using CMB for the removal of Pb from water is proposed as an effective, environmentally protective, novel approach.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...