Hybrid analytical-numerical approach for investigation of differential effects in normal and cancer cells under electroporation†
Abstract
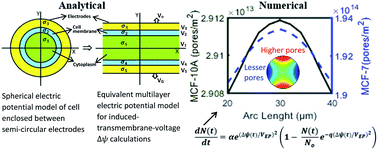
Electroporation has offered important biomedical applications in electrochemotherapy, tissue ablation and gene editing recently. Time and computation efficient analytical and numerical models should be developed to understand the differential effects of electroporation on normal and cancer cells. In this work, we present a hybrid analytical–numerical approach to investigate the behavior of normal and cancer cells under electroporation. We have compared the human breast cancer cell (MCF-7) and non-tumorigenic human breast cell (MCF-10A) under electroporation in terms of change in transmembrane voltage and pore formation on cell surface. The effects of electric pulse time, amplitude and membrane conductivity variation are analyzed in a systematic manner. To accelerate the calculation of transmembrane voltage, we have introduced a simple Multilayer Electric Potential Model (MEPM) which calculates the potential distribution across the cell analytically. The MEPM calculates electric potential distribution across a biological cell sandwiched between two semi-circular electrodes held at fixed potential, by solving the Laplace's equation over an equivalent planar, multilayer geometry. The MEPM model is then used in a Finite Element Method (FEM) based numerical model of electroporation. Transmembrane voltage and pore density for electroporated MCF-10A are estimated to be 1.31 V and 2.98 × 1013 m−2 respectively, and for MCF-7 the estimated values are 0.53 V and 1.93 × 1014 m−2, respectively. Our results suggest that under electroporation, the cancer cell's membrane get much more permeabilized than its counterpart normal cell even at small values of transmembrane voltage. This work provides a theoretical basis for further experimental exploration of electroporation process in cancer therapy, and serves as a design tool for performance optimization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...