Sulfation effect of Ce/TiO2 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: mechanism and kinetic studies†
Abstract
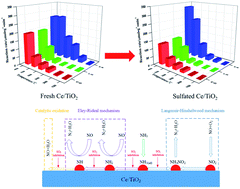
Ceria-based catalysts are competitive substitutes for the commercial SCR catalysts due to their high SCR activity and excellent redox performance. For a better understanding of the SO2 poisoning mechanism over ceria-based catalysts, the sulfation effect of the Ce/TiO2 catalyst on the SCR activity over a wide reaction temperature range was systematically studied via comprehensive characterizations, in situ DRIFT studies and kinetic studies. The results demonstrated that the NO conversion at 150 °C is significantly inhibited by the formation of cerium sulfites/sulfates due to the inhibited redox properties and excessive adsorption of NH3, which restrict the dissociation of NH3 to NH2, resulting in a much lower reaction rate of E–R reaction over the sulfated Ce/TiO2 catalyst. With the increase in the reaction temperature, the reaction rate of the E–R reaction significantly increased due to the improved redox properties and weakened adsorption of NH3. Moreover, the rate of the C–O reaction over the sulfated Ce/TiO2 catalysts is obviously lower than that of the fresh Ce/TiO2 catalyst. The promotion of NO conversion over the sulfated catalyst at 330 °C is attributed to both the increase in the reaction rate of E–R reaction and the inhibition of the C–O reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...