The rapid effects of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) enriched phospholipids on alleviating exercise fatigue in mice
Abstract
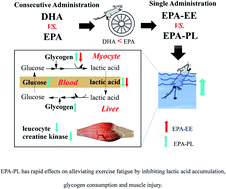
It has been reported that docosahexaenoic acid/eicosapentaenoic acid (DHA/EPA) and phospholipids (PLs) play an important role in alleviating exercise fatigue. However, the difference of DHA and EPA in ameliorating exercise fatigue is still unclear. Furthermore, the comparative study about DHA/EPA-PLs and nonpolar DHA/EPA on exercise fatigue has not been reported. In the present study, the effects of DHA and EPA on exercise fatigue was firstly compared by conducting an exhaustion test, and the results showed that triglyceride (TG) with high ratio of EPA had a more significant effect on alleviating exercise fatigue than TG with a low ratio of EPA in mice. Therefore, eicosapentaenoic acid–ethyl ester (EPA–EE) and EPA–PL were then selected to compare the rapid effects of polar and nonpolar DHA/EPA on exercise fatigue in mice by a weight-loaded swimming exhaustion test. A single intake of EPA–PL but not EPA–EE significantly alleviated exercise fatigue in mice by increasing the lactic acid recycling rate as well as inhibiting glycogen consumption and muscle injury, suggesting that EPA–PL exhibited a rapid effect on alleviating exercise fatigue. The study might represent a potential novel candidate or targeted dietary pattern for alleviating exercise fatigue.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...