Highly improved photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B over Bi2Ga4−xFexO9 solid solutions under visible light irradiation†
Abstract
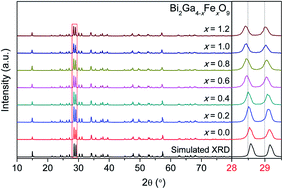
In this work, Bi2Ga4−xFexO9 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1.2) solid solutions were prepared via the traditional high-temperature solid-state reaction. The Le Bail fitting on the powder X-ray diffraction patterns shows that these solid solutions were successfully synthesized. Scanning electron microscopy showed that the Bi2Ga3.2Fe0.8O9 sample was composed of sub-micron particle crystallites. Energy dispersive spectroscopy analysis and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were used to identify that the Fe element is trivalent when doping into the crystal structure. Ultraviolet-visible diffused reflectance spectra suggested that the bandgap of Bi2Ga3.2Fe0.8O9 is narrower than that of the undoped Bi2Ga4O9 sample. Three strategies, including Fe3+ doping, addition of H2O2, and loading of the cocatalyst, were utilized to improve the photocatalytic degradation activity. The optimum photocatalytic performance was obtained over 2.5 wt% Cu/Bi2Ga3.2Fe0.8O9 sample in 20 ppm RhB aqueous solution (containing 1.5 mL H2O2) under visible light irradiation. Its photodegradation rate is 8.0 times that of Bi2Ga4O9 containing 0.5 mL H2O2. The 2.5 wt% Cu/Bi2Ga3.2Fe0.8O9 photocatalyst remained stable and active even after four cycles. Also, its photocatalytic conversion efficiency for RhB was nearly 100%, which was achieved in 3 hours. The photocatalytic mechanism indicated that ·OH and h+ played an important role in the photocatalytic degradation reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...