Zwitterionic superabsorbent polymer hydrogels for efficient and selective removal of organic dyes†
Abstract
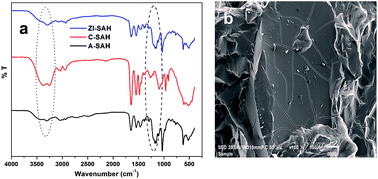
A novel zwitterionic superabsorbent polymer hydrogel [ZI-SAH] was synthesized by free radical polymerization and used for the removal of crystal violet (CV) and congo red (CR) from an aqueous medium. ZI-SAH was composed of pH-sensitive monomers poly(3-acrylamidopropyl) trimethylammoniumchloride (APTMACl) and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulphonic acid (AAMPSA). The hydrogel was characterized by SEM and FT-IR spectroscopy, while the visco-elastic behavior was studied using rheological tests. The hydrogel showed a point of zero charge (PZC) at pH 7.2 and high swelling abilities of 3715% at pH 9 and 3112% at pH 5. The cationic crystal violet (CV) and anionic congo red (CR) dyes were employed to investigate the removal ability of ZI-SAH using the batch adsorption method. The materials became more selective towards oppositely charged dyes at pH 5 and 9. The effects of parameters such as contact time, initial concentration of dyes, pH, ZI-SAH dosage and ionic strength on the removal performance were investigated. A kinetic study was carried out via Lagergren pseudo first order and pseudo second order kinetics. The adsorption efficiencies of ZI-SAH were 13.6 mg g−1 for CV and 9.07 mg g−1 for CR with % removal values of 97 and 89, respectively. The thermodynamic parameters, namely, ΔG°, ΔH° and ΔS° were determined, and the negative value of free energy showed that the process of adsorption was spontaneous. ZI-SAH was recycled and reused in five consecutive cycles with removal efficiency > 75%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...