Effects of lipid composition on membrane distribution and permeability of natural quinones†
Abstract
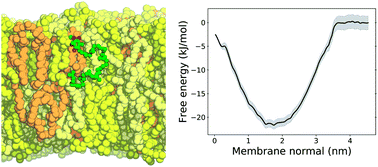
Natural quinones are amphiphilic molecules that function as mobile charge carriers in biological energy transduction. Their distribution and permeation across membranes are important for binding to enzymatic complexes and for proton translocation. Here, we employ molecular dynamics simulations and free energy calculations with a carefully calibrated classical force-field to probe quinone distribution and permeation in a multi-component bilayer trying to mimic the composition of membranes involved in bioenergetic processes. Ubiquinone, ubiquinol, plastoquinone and menaquinone molecules with short and long isoprenoid tails are simulated. We find that penetration of water molecules bound to the polar quinone head increases considerably in the less ordered and porous bilayer formed by di-linoleoyl (18:2) phospholipids, resulting in a lower free energy barrier for quinone permeation and faster transversal diffusion. In equilibrium, quinone and quinol heads localize preferentially near lipid glycerol groups, but do not perform specific contacts with lipid polar heads. Quinone distribution is not altered significantly by the quinone head, tail and lipid composition in comparison to a single-component bilayer. This study highlights the role of lipid acyl chain unsaturation for permeation and transversal diffusion of polar molecules across biological membranes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating Latin American Talent in Chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...