Rechargeable aluminum batteries: effects of cations in ionic liquid electrolytes†
Abstract
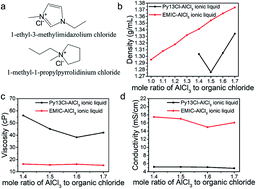
Room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) are solvent-free liquids comprised of densely packed cations and anions. The low vapor pressure and low flammability make ILs interesting for electrolytes in batteries. In this work, a new class of ionic liquids were formed for rechargeable aluminum/graphite battery electrolytes by mixing 1-methyl-1-propylpyrrolidinium chloride (Py13Cl) with various ratios of aluminum chloride (AlCl3) (AlCl3/Py13Cl molar ratio = 1.4 to 1.7). Fundamental properties of the ionic liquids, including density, viscosity, conductivity, anion concentrations and electrolyte ion percent were investigated and compared with the previously investigated 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride (EMIC-AlCl3) ionic liquids. The results showed that the Py13Cl–AlCl3 ionic liquid exhibited lower density, higher viscosity and lower conductivity than its EMIC-AlCl3 counterpart. We devised a Raman scattering spectroscopy method probing ILs over a Si substrate, and by using the Si Raman scattering peak for normalization, we quantified speciation including AlCl4−, Al2Cl7−, and larger AlCl3 related species with the general formula (AlCl3)n in different IL electrolytes. We found that larger (AlCl3)n species existed only in the Py13Cl–AlCl3 system. We propose that the larger cationic size of Py13+ (142 Å3) versus EMI+ (118 Å3) dictated the differences in the chemical and physical properties of the two ionic liquids. Both ionic liquids were used as electrolytes for aluminum–graphite batteries, with the performances of batteries compared. The chloroaluminate anion-graphite charging capacity and cycling stability of the two batteries were similar. The Py13Cl–AlCl3 based battery showed a slightly larger overpotential than EMIC-AlCl3, leading to lower energy efficiency resulting from higher viscosity and lower conductivity. The results here provide fundamental insights into ionic liquid electrolyte design for optimal battery performance.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Battery development over the last decade and Editors' Collection: Lithium-ion batteries and beyond - materials, processes and recycling


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...