Metformin promotes proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in Ox-LDL stimulated macrophages by regulating the miR-34a/Bcl2 axis†
Abstract
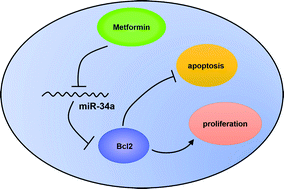
Background: Metformin, an antidiabetic drug, has been reported to be involved in atherosclerosis (AS). In this study, the effects of metformin on oxidized low-density lipoprotein (Ox-LDL)-induced macrophage apoptosis were investigated, and the mechanisms involved in this process were examined. Methods: qRT-qPCR analysis was performed to detect the expression of miR-34a in macrophage cells. Cell proliferation was determined by MTT assays and colony formation assays. Cell apoptosis was assessed by the detection of apoptotic rate and caspase 3 activity. Western blot analysis was performed to evaluate the expression of Bcl2 protein. Results: Metformin treatment promoted proliferation and suppressed apoptosis in macrophages following the treatment of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (Ox-LDL). Metformin could inhibit miR-34a in macrophages. miR-34a overexpression could reverse the effect of metformin on proliferation and apoptosis in Ox-LDL-treated macrophages. Moreover, metformin could increase the expression of the miR-34a target gene Bcl2. Furthermore, metformin treatment exerted the pro-proliferation and anti-apoptosis effect through regulating Bcl2 expression in Ox-LDL-stimulated macrophages. Conclusion: Metformin facilitated proliferation and inhibited apoptosis of macrophages treated with Ox-LDL through the miR-34a/Bcl2 axis, indicating the potential value of metformin in AS therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...