One-pot synthesized Cu/Au/Pt trimetallic nanoparticles as a novel enzyme mimic for biosensing applications†
Abstract
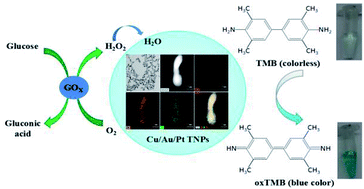
Multimetallic nanomaterials have aroused special attention owing to the unique characteristics of chemical, optical and enhanced enzyme mimetic capabilities resulting from the synergistic effect of different metal elements. In this work, we present a facile, gentle, fast and one-pot method for preparing Cu/Au/Pt trimetallic nanoparticles (TNPs), which possess intrinsic and enhanced peroxidase-like activity as well as excellent stability, sustainable catalytic activity, and robustness to harsh environments. Kinetic analysis indicated that Cu/Au/Pt TNPs exhibited strong affinities with H2O2 and 3,3,5,5-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) as the substrates. To investigate the feasibility of Cu/Au/Pt TNPs-based strategy in biological analysis, H2O2 was chosen as a model analyte and a sensitive and specific detection for H2O2 was acquired with a detection limit of 17 nM. By coupling with glucose oxidase (GOD), this assay could also achieve a sensitive and selective detection of glucose with a detection limit of 33 μM, indicating the versatility of the method. In view of the potential combination with diverse enzyme-related reactions, the Cu/Au/Pt TNPs-based strategy is promising as a universal platform for biosensors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...