Endosomal/lysosomal location of organically modified silica nanoparticles following caveolae-mediated endocytosis
Abstract
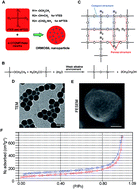
Organically modified silica (ORMOSIL) nanoparticles (NPs) are widely used in biomedicine. However, their cell uptake process has not yet been characterised in detail. Here, we investigated the mechanism underlying endocytosis and subcellular localisation of ORMOSIL NPs. Exposure to ORMOSIL NPs induced a decrease in cell viability and increase in lactate dehydrogenase release in a dose-dependent manner in A549 cells. Once internalised, ORMOSIL NPs were translocated from early endosomes to the lysosomes, where they accumulated. Furthermore, deficiency of autophagosomal/lysosomal fusion failed to block lysosomal localisation of ORMOSIL NPs, suggesting that autophagy was not involved in the final lysosomal accumulation of ORMOSIL NPs. Meanwhile, an inhibitor of caveolae-mediated endocytosis, rather than inhibitors of phagocytosis or clathrin-mediated endocytosis, succeeded in blocking ORMOSIL NP cell uptake, indicating the involvement of caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Together, these results provide a new understanding of the toxicity, and suggest better biomedical applications, of ORMOSIL NPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...