In situ polymerization and FT-IR characterization of poly-glycine on pencil graphite electrode for sensitive determination of anti-emetic drug, granisetron in injections and human plasma†
Abstract
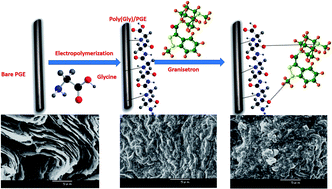
In situ polymerization is a simple and efficient technique for modification and fabrication of modified electrodes in voltammetry. An efficient and highly sensitive square wave voltammetric (SWV) method was developed for analysis of a 5-HT3 antagonist granisetron (GRN) using in situ polymerized glycine on pencil graphite electrode surface. It was found that the fabricated polymer enhanced the sensitivity by more than two times and enhanced the surface activity by more than three times. Surface area measurements showed that poly-Gly/PGE have large surface area of 44.3 mm2, when compared to that of bare PEG (12.1 mm2). Several methods as cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) techniques were used to characterize the modified surface. Further, FT-IR spectroscopic study was used to predict the way of glycine polymerization on electrode surface and the possible interaction mechanism with GRN. After optimization, the proposed method showed a linear response of GRN concentrations in the range from 0.08 to 3.00 μmol L−1 with a limit of detection (LOD) of 26.2 nmol L−1 (9.14 ng mL−1). The method was utilized for GRN determination in ampoules and in real human plasma samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...