Novel sulfonamidospirobifluorenes as fluorescent sensors for mercury(ii) ion and glutathione†
Abstract
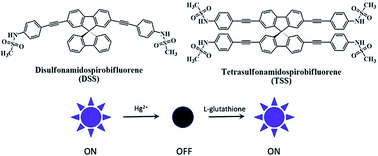
Novel spirobifluorene derivatives containing two and four sulfonamide groups are successfully synthesized from the commercially available bromo-9,9′-spirobifluorene by Sonogashira couplings. These compounds exhibit an excellent selective fluorescence quenching by Hg(II) in DMSO/HEPES buffer mixture with three-times-noise detection limits of 10.4 to 103.8 nM. A static aggregation induced quenching mechanism is proposed based on the data from 1H-NMR and UV-Vis spectroscopy, as well as the observation of the Tyndall effect. Quantifications of Hg(II) using these sensors are in good agreement with those obtained from ICP-OES. The reversibility of these sensors is demonstrated by a complete fluorescence restoration upon addition of EDTA or L-glutathione. The application as a turn-on sensor for L-glutathione is demonstrated in a quantitative analysis of three samples of L-glutathione supplement drinks.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...