Plasmonic nanomaterial structuring for SERS enhancement
Abstract
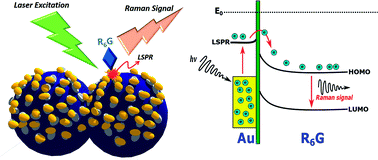
Unique structures of a gold island over nanospheres (AuIoN) featuring a three-dimensional (3D) nanostructure on a highly ordered two-dimensional (2D) array of nanospherical particles with different adhesion layers were fabricated as surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates. Ultra-thin Au was thermally evaporated onto PS nanospheres while aluminum oxide (Al2O3) was applied as an Au adhesion layer. The outcomes demonstrate that the higher metallic particle density and surface roughness supplied by the Al2O3 provided larger interatomic bonding than a conventional adhesion layer, the highly-dispersive Cr. Nanosphere lithography (NSL) to deposit templating particles as small as ∼100 nm successfully created a simple initial roughening process which in turn boosted the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) efficiency. So far, PS template deposition of a size less than 200 nm has been challenging, but here, through the use of a simple solvent ratio adjustment on drop-casting NSL, the novelty of natural lithography with downscaled properties as an alternative to the complexity of photolithography which is mostly conducted in the strict ambience of a clean room, is presented. SERS activity was primarily attributed to the synergistic effect of collective LSPRs from the AuIoN structure reinforcing the electromagnetic field, particularly in the crevices of two neighboring AuIoNs, as simulated by FDTD (Finite-Difference Time-Domain) computation. An AuIoN fabricated by the integration of Al2O3 with thinner Au particles showed the optimum SERS activities with an improved enhancement factor of 1.51 × 106. Overall, a non-lithographic technique in tuning SERS hotspots and favorable characteristics of Al2O3 for ultra-thin Au adhesion support, which can potentially be used in the fabrication of various devices, was demonstrated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...