Catalytic decomposition of N2O over Cu–Al–Ox mixed metal oxides
Abstract
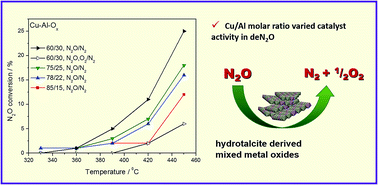
Cu–Al–Ox mixed metal oxides with intended molar ratios of Cu/Al = 85/15, 78/22, 75/25, 60/30, were prepared by thermal decomposition of precursors at 600 °C and tested for the decomposition of nitrous oxide (deN2O). Techniques such as XRD, ICP-MS, N2 physisorption, O2-TPD, H2-TPR, in situ FT-IR and XAFS were used to characterize the obtained materials. Physico-chemical characterization revealed the formation of mixed metal oxides characterized by different specific surface area and thus, different surface oxygen default sites. The O2-TPD results gained for Cu–Al–Ox mixed metal oxides conform closely to the catalytic reaction data. In situ FT-IR studies allowed detecting the form of Cu+⋯N2 complexes due to the adsorption of nitrogen, i.e. the product in the reaction between N2O and copper lattice oxygen. On the other hand, mostly nitrate species and NO were detected but those species were attributed to the residue from catalyst synthesis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...