Cycloaddition of atmospheric CO2 to epoxides under solvent-free conditions: a straightforward route to carbonates by green chemistry metrics
Abstract
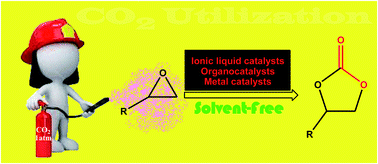
The conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) into value-added organic compounds has received more and more attention over recent years, not only because this gas is one of the major anthropogenic greenhouse gases, but also because it has been regarded as an abundant, inexpensive, nontoxic, nonflammable, and renewable one-carbon (C1) resource. Along these lines, the synthesis of five-membered cyclic carbonates employing CO2 as a safe alternative to toxic reagents such as phosgene or its derivatives is of great interest because of their wide range of applications in organic synthesis. However, most of CO2 incorporation reactions into carbonates are carried out in toxic and non-recyclable organic solvents. Furthermore, these transformations usually proceed at elevated pressures or supercritical CO2 conditions. Recently, several catalytic systems have been developed that allow the synthesis of functionalized carbonates from the reaction of atmospheric CO2 with corresponding epoxides under solvent-free conditions. This review is an attempt to summarize the most important advances and discoveries in this interesting research arena. The review is divided into three major sections. The first section will discuss ionic liquid catalyzed coupling reactions. The second will cover organocatalyzed reactions. The third focuses exclusively on metal-catalyzed fixations. Notably, the third section has been classified based on the metal element that carries out the catalysis (i.e. copper, palladium, zinc).
- This article is part of the themed collection: Sustainable synthesis


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...