Nitrogen oxide removal by non-thermal plasma for marine diesel engines
Abstract
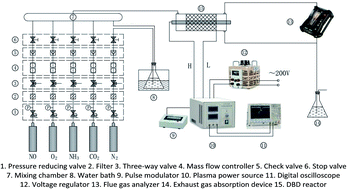
The transportation industry plays an important role in the world economy. Diesel engines are still widely used as the main power generator for trucks, heavy machinery and ships. Removal technology for nitrogen oxides in diesel exhaust are of great concern. In this paper, a gas supply system for simulating the marine diesel engine exhaust is set up. An experimental study on exhaust denitration is carried out by using a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) reactor to generate non-thermal plasma (NTP). The power efficiency and the denitration efficiency of different gas components by NTP are discussed. The exhaust gas reaction mechanism is analyzed. The application prospects of NTP are explored in the field of diesel exhaust treatment. The experimental results show that the power efficiency and energy density (ED) increase with the input voltage for this system, and the power efficiency is above 80% when the input voltage is higher than 60 V. The removal efficiency of NO is close to 100% by NTP in the NO/N2 system. For the NO/O2/N2 system, the critical oxygen concentration (COC) increases with NO concentration. The O2 concentration plays a decisive role in the denitration performance of the NTP. H2O contributes to the oxidative removal of NO, and NH3 improves the removal efficiency at low ED while slightly reducing the denitration performance at high ED. CO2 has little effect on NTP denitration performance, but as the ED increases, the generated CO gradually increases. When simulating typical diesel engine exhaust conditions, the removal efficiency increases first and then decreases with the increase of ED in the NO/O2/CO2/H2O/N2 system. After adding NH3, the removal efficiency of NOx reaches up to 40.6%. It is necessary to add reducing gas, or to combine the NTP technology with other post treatment technologies such as SCR catalysts or wet scrubbing, to further increase the NTP denitration efficiency.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...