A chemical-bond-driven edge reconstruction of Sb nanoribbons and their thermoelectric properties from first-principles calculations†
Abstract
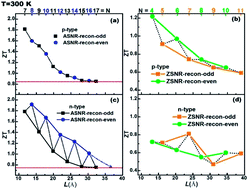
We present a theoretical study on the potential thermoelectric performance of antimony nanoribbons (SNRs). Based on density functional theory and the semiclassical transport model, the thermoelectric figure of merit ZT was calculated for various Sb nanoribbon sizes and different chiralities. The results indicated that the chemical-bond-driven edge reconstruction of nanoribbons (denoted as SNRs-recon) eliminated all of the dangling bonds and passivated all of the boundary antimony atoms with 3-fold coordination. SNRs-recon are the most energy favorable compared to the ribbons with unsaturated edge atoms. Semimetal to semiconductor transition occurred in SNRs-recon. The band gap was width-dependent in armchair SNRs (denoted as ASNRs-recon), whereas it was width-independent in zigzag SNRs (ZSNRs-recon). After nanolization and reconstruction, the TE properties of SNRs were enhanced due to higher Seebeck coefficient and lower thermal conductivity. The thermoelectric properties of n-doped ASNRs-recon and p-doped ZSNRs-recon showed width-dependent odd–even oscillation and eventually resulted in ZT values of 0.75 and 0.60, respectively. Upon increasing the ribbon width, ZT of n-doped ASNRs-recon decreased and approached a constant value of about 0.85. However, n-doped ZSNRs-recon exhibited poor TE performance compared with the others. Importantly, the ZT value could be optimized to as high as 1.91 at 300 K, which was larger than those of Sb-based bulk materials and 100 times that of thin Sb films. These optimizations make the materials promising room-temperature high-performance thermoelectric materials. Furthermore, the proposed new concept of chemical-bond-driven edge reconstruction may be useful for many other related systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...