A novel electrolyte additive for improving the interfacial stability of LiMn2O4 cathode lithium-ion batteries at elevated temperature†
Abstract
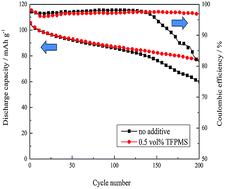
Methanesulfonic acid 2,2,3,3-tetrafluoropropyl (TFPMS) is newly explored as a protection additive to improve the interfacial stability of LiMn2O4 cathode/electrolyte at an elevated temperature. At 1C rate, the addition of 0.5 vol% TFPMS improves the capacity retention of an LiMn2O4/Li cell from 56.9% to 72.9% after 200 cycles at 55 °C. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) results suggest that the electrolyte with 0.5 vol% TFPMS forms a thinner and less resistive interface. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis reveals that the addition of TFPMS restrains the formation of LiF and Li2CO3. Moreover, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and inductively coupled plasma (ICP) analysis confirms the effectiveness of TFPMS-enhanced structural stability of LiMn2O4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...