Hydration of phenylacetylene on sulfonated carbon materials: active site and intrinsic catalytic activity†
Abstract
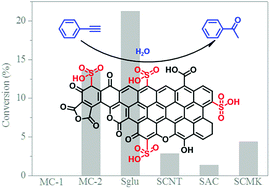
A series of sulfonated carbon materials (sulfonated glucose-derived carbon, carbon nanotubes, activated carbon and ordered mesoporous carbon, denoted as Sglu, SCNT, SAC and SCMK, respectively) were synthesized and applied as acid catalysts in phenylacetylene (PA) hydration reactions. The sulfonic acid groups (–SO3H) were identified to be the only kind of active sites and were quantified with XPS and a cation exchange process. Mechanistic studies revealed that the catalytic PA hydration reaction follows pseudo first order reaction kinetics. Sglu exhibits a higher reaction rate constant (k) and lower apparent activation energy (Ea) in the hydration reactions than SCNT catalysts. NH3-temperature programmed desorption measurement results revealed that the relatively high catalytic activity of Sglu was attributed to both the stronger acidity and larger number of –SO3H active sites. This work exhibited the performance of carbon materials without any extra acidic additives in PA hydration reaction and investigated the intrinsic catalytic activity by kinetics. The present work provides the possibility for acid catalytic applications of carbon materials, which sheds light on the environmentally friendly and sustainable production strategy for aldehyde ketone compounds via the catalytic alkyne hydration reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...