A novel information diffusion method based on network consistency for identifying disease related microRNAs
Abstract
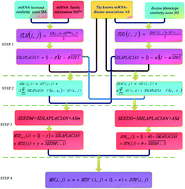
The abnormal expression of miRNAs is directly related to the development of human diseases. Predicting the potential candidate miRNAs associated with diseases can contribute to the detection, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of human complex diseases. The effective inference of the calculation method of the relationship between miRNAs and diseases is an effective supplement to biological experiments. It is of great help in the prevention, treatment and prognosis of complex diseases. This paper proposes a novel information diffusion method based on network consistency (IDNC) for identifying disease related microRNAs. The model first synthesizes the miRNA family information and the miRNA function similarity to reconstruct the miRNA network, and reconstruct the disease network by using the known disease and miRNA-related information and the semantic score between diseases. Then the global similarity of the two networks is obtained by using the Laplacian score of graphs. The global similarity score is a measure of the similarity between diseases and miRNAs. The disease–miRNA relation network was reconstructed by integrating the global similarity relation. The network consistency diffusion seed is then obtained by combining the global similarity network with the reconstructed disease–miRNA association network. Thereafter, the stable diffusion spectrum is generated as the prediction score by using the restarted random walk algorithm. The AUC value obtained by performing the LOOCV in the gold benchmark dataset is 0.8814. The AUC value obtained by performing the LOOCV in the predictive dataset is 0.9512. Compared with other frontier methods, our method has higher accuracy, which is further illustrated by case studies of breast neoplasms and colon neoplasms to prove that IDNC is valuable.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...