Theoretical analyses on water cluster structures in polymer electrolyte membrane by using dissipative particle dynamics simulations with fragment molecular orbital based effective parameters†
Abstract
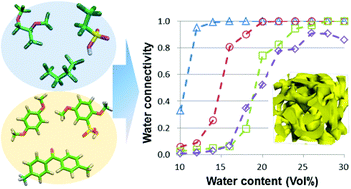
The mesoscopic structures of polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) affect the performances of fuel cells. Nafion® with the Teflon® backbone has been the most widely used of all PEMs, but sulfonated poly-ether ether-ketone (SPEEK) having an aromatic backbone has drawn interest as an alternative to Nafion. In the present study, a series of dissipative particle dynamics (DPD) simulations were performed to compare Nafion and SPEEK. These PEM polymers were modeled by connected particles corresponding to the hydrophobic backbone and the hydrophilic moiety of sulfonic acid group. The water particle interacting with Nafion particles was prepared as well. The crucial interaction parameters among DPD particles were evaluated by a series of calculations based on the fragment molecular orbital (FMO) method in a non-empirical way (Okuwaki et al., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2018, 122, 338–347). Through the DPD simulations, the water and hydrophilic particles aggregated, forming cluster networks surrounded by the hydrophobic phase. The structural features of formed water clusters were investigated in detail. Furthermore, the differences in percolation behaviors between Nafion and SPEEK revealed much better connectivity among water clusters by Nafion. The present FMO-DPD simulation results were in good agreement with available experimental data.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...