Boron carbide composites with highly aligned graphene nanoplatelets: light-weight and efficient electromagnetic interference shielding materials at high temperatures
Abstract
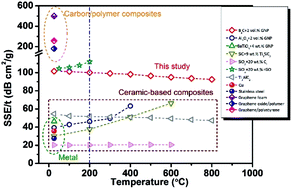
B4C-based ceramic composites containing 0–2 vol% highly aligned graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) are fabricated. The electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding properties of the obtained composites are investigated at X-band (8.2–12.4 GHz) frequency range from room-temperature up to 800 °C. All composites exhibit outstanding EMI shielding properties with satisfactory frequency- and thermal-stability. The shielding effectiveness (SE) of GNP/B4C composites increases monotonically with increasing GNP loading. Superior room-temperature SE close to 40 dB is achieved with only 2 vol% GNPs and high SE around 35 dB still persists at 800 °C. Considering their relatively low density, GNP/B4C composites possess a high specific shielding effectiveness (SSE) of 16 dB cm3 g−1 which is among the highest values in reported ceramic-based shielding composites. Especially, the GNP/B4C composite with 2 vol% GNPs exhibits the highest SSE/t (SSE divided by thickness) values at temperatures above 200 °C for all reported shielding composites, indicating that GNP/B4C composites belong to the most promising high-temperature shielding composites. The excellent shielding properties of GNP/B4C composites arise mainly from the high electrical conductivity, high dielectric loss and the multiple reflections by the highly aligned and large-sized GNP layers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...