Determination of major and trace element variability in healthy human urine by ICP-QMS and specific gravity normalisation†
Abstract
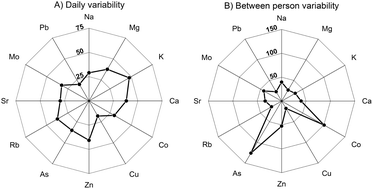
Sixty five urine samples obtained during one or two non-consecutive days from 10 healthy individuals were analysed for major (Na, Mg, K, Ca) and trace (Co, Cu, Zn, As, Rb, Sr, Mo and Pb) element concentrations. Following microwave digestion, the analyses were carried out using ICP-QMS (inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass spectrometry) incorporating a collision/reaction cell. Repeat analyses of quality control samples show that the procedure produces unbiased results and is well suited for routine urinalysis of the investigated elements. Concentrations were normalised using specific gravity (SG) and the resultant decrease in variability supports previous conclusions that SG-normalisation appropriately corrects for differences in urine dilution. The elemental concentrations of the individual urine samples show large differences in dispersion. Most variable are As, Co and Zn, with CVs (coefficients of variation) of >75%. The major elements as well as Rb, Sr and Mo display intermediate variability, whilst Cu and Pb have the least elemental dispersion with CV values of about 30%. A detailed assessment shows that the overall elemental variability is governed both by differences between individuals and variations for a single individual over time. Spot urine samples exhibit elemental concentrations that, on average, resemble the daily mean values to within about 30% for all elements except K and Rb. Diet-related changes in urinary element concentration are most prominent for Mg, K, Co, Rb and Pb. The concentrations of Co, As and Rb appear to vary systematically with gender but this may primarily reflect co-variance with specific diets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...