Improving the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO for TiO2 hollow spheres through hybridization with a cobalt complex†
Abstract
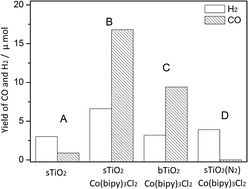
A chemical system with enhanced efficiency for electron generation and transfer was constructed by the integration of TiO2 hollow spheres with [Co(bipy)3]2+. The introduction of [Co(bipy)3]2+ remarkably enhances the photocatalytic activity of pristine semiconductor photocatalysts for heterogeneous CO2 conversion, which is attributable to the acceleration of charge separation. Of particular interest is that the excellent photocatalytic activity of the heterogeneous catalysts can be utilised for a universal photocatalytic CO2 reduction system. Yields of 16.8 μmol CO and 6.6 μmol H2 can be obtained after 2 h of the photoredox reaction, and the apparent overall quantum yield was estimated to be 0.66% under irradiation at λ = 365 nm. The present findings clearly demonstrate that the integration of electron mediators with semiconductors is a feasible process for the design and development of efficient photochemical systems for CO2 conversion.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Editors' collection: Carbon Dioxide Capture/Reduction


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...