Affinity binding of chicken apolipoprotein A1 to a novel flax orbitide (linusorb)
Abstract
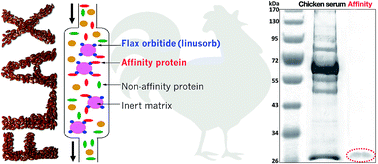
Bioactive orbitides (linusorbs, LOs) from flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) were ligated through methionine with resin to form an affinity column. The affinity resin was characterized using elemental analysis and the resin bound 70% of its weight in LOs. Chicken serum was passed over the column and washed to remove non-binding materials. The column was eluted with unbound orbitide to competitively release bound protein. A single 28 kDa protein was found in the affinity binding pool. The protein MW and sequence were identical to apolipoprotein A1 (Apo A1), a major serum protein. Its role includes reverse cholesterol transport and cholesterol efflux. The affinity technique allowed convenient and rapid isolation of Apo A1 with a recyclable affinity column. LO binding to a cholesterol carrier molecule might also help us to understand the mechanism of action of LOs in health and the biological activity of flaxseed products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...