Rapid quantitation of multiple ions released from HeLa cells during emodin induced apoptosis by low-cost capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection
Abstract
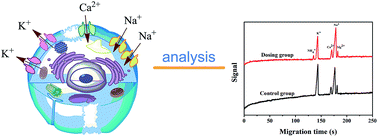
Change in cation concentration, including that of potassium and sodium, is characteristic of apoptosis, therefore it is significant to detect cation concentration changes. In this work a rapid, sensitive, and practical method was developed for the determination of Na+ and K+ concentration in HeLa cells during emodin induced apoptosis by a low-cost capillary electrophoresis device with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection (CE-C4D). Under the optimized conditions, both ions were baseline separated in 4 min with 40 mM MES/40 mM His containing 1 mM 18-crown-6 as the separation buffer at pH 6.0. The limit of detections (LODs) and limit of quantifications (LOQs) were 0.47–1.15 μM and 1.58–3.86 μM, respectively. The precision for migration times and peak areas was below 0.56% and 3.74%, respectively. The data proved that the concentration of cations in cells can be accurately quantified. It was found that the K+ concentration decreased from 82.2 μM to 52.7 μM, and the Na+ concentration increased from 62.4 μM to 127.2 μM during the process of apoptosis when the cell density was 1 × 105 cells per mL. The low-cost CE-C4D provides a convenient way to decipher the interaction of Na+ and K+ in the regulation of cell apoptosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...