Characterizing the binding interaction of astilbin with bovine serum albumin: a spectroscopic study in combination with molecular docking technology
Abstract
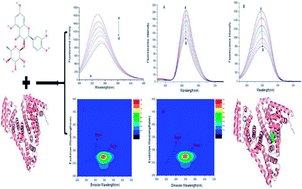
Astilbin (ASN) is a flavonoid compound isolated from the rhizome of Smilax china L. (Smilacaceae). It has many bioactivities, such as selective immunosuppression, antioxidant, anti-hepatic injury, etc., and is widely used in traditional Chinese medical treatments. The interaction of ASN with bovine serum albumin (BSA) was studied in a physiological buffer (pH = 7.40) using multi-spectroscopic techniques in combination with molecular docking methods. UV-vis absorption measurements proved that a ASN–BSA complex could be formed. Fluorescence data revealed that ASN could strongly quench the intrinsic fluorescence of BSA in terms of a static quenching procedure. The process of binding was spontaneous and the binding occurred mainly through hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces. The distance r between donor (BSA) and acceptor (ASN) was calculated to be 4.80 nm based on Förster's non-radiative energy transfer theory. The binding constant (Ka = 7.31 × 104 mol L−1) and the number of binding sites (n ≈ 1) at 298 K suggested that ASN only occupied one site in BSA with high affinity. Moreover, the results of molecular docking indicated that ASN was more likely to be located in site I (sub-domain IIA) of BSA. The results of synchronous fluorescence and three-dimensional fluorescence spectra showed that ASN induced conformational changes of BSA. The findings would be beneficial for research on the transportation, distribution and some important bioactivities of ASN in the human body.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...