Enzymatic hydrogelation of self-assembling peptide I4K2 and its antibacterial and drug sustained-release activities†
Abstract
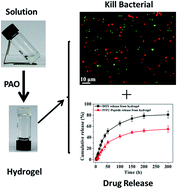
Hydrogels provide great potential for biomedical applications. For clinical use, hydrogels could be used as scaffold materials for cell culture, regenerative medicine and drugs release with bactericidal properties. The amphiphilic peptide I4K2 is designed to inhibit bacterial growth through membrane permeation mechanisms. I4K2 is found to be able to self-assemble into nanofibers and form hydrogels in the presence of an enzyme (plasma amine oxidase, PAO). HPLC and MALDI-TOF-MS data show that PAO promoted the oxidation of the ε-amine of the lysine side chain. The cross-linking of I4K2 molecules catalyzed by PAO leads to a decrease in the amount of the positive charge of the system, which enhances the interaction between the self-assembled nanofibers and contributes to the formation of hydrogels. This self-supported hydrogel showed antibacterial activity against both G+ and G− bacteria and has low cytotoxicity, which enable it be consequently used as an antimicrobial agent or biological engineering scaffold material. The hydrogel also possesses good drug sustained-release activities. These advantages result in the great potential of this enzymatic I4K2 hydrogel for biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...