Adsorption and separation properties of positively charged ZrO2 nanofibrous membranes fabricated by electrospinning
Abstract
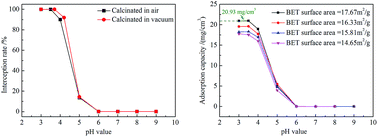
As a new type of adsorption and separation materials, positively charged ceramics exhibit the advantages of safety and high separation efficiency. However, these materials possess low specific surface area and adsorption capacity. In this study, positively charged ZrO2 nanofibrous membranes were fabricated by electrospinning and calcination. The membranes were characterized in terms of morphology, composition, and pore structure. The adsorption and separation performance of the membranes on titan yellow solution was also investigated. Overlapping electrospun nanofibers formed nanofibrous membranes with porous structures (pore size of 0.2–1.6 μm) and a high specific surface area. Increasing the nanofiber diameter decreased the specific surface area of the nanofibrous membranes, and vacuum calcination increased their surface positive charge. The maximum flux of the positively charged ZrO2 nanofibrous membranes reached 523 L (m2 h)−1, and the interception rate for titan yellow was 99.997%. The saturated adsorption capacity of vacuum-calcined ZrO2 nanofibrous membranes increased with increasing specific surface area, and their maximum adsorption capacity reached 20.93 mg cm−3.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...