Adsorptive removal of aqueous bezafibrate by magnetic ferrite modified carbon nanotubes†
Abstract
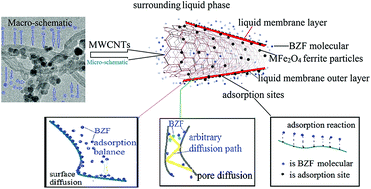
In this work, magnetic ferrite modified carbon nanotubes (MFe2O4/CNTs, M: Mn or Co) were synthesized and employed as adsorbents to remove emerging pollutant bezafibrate (BZF) from aqueous solution. The structural and surface properties of the prepared adsorbents were characterized, and the performances of the MFe2O4/CNTs were systematically investigated from adsorption kinetics and mechanistic points of view. Results showed that the fabricated MFe2O4/CNTs could integrate the advantages of CNTs and ferrite, thereby exhibiting an excellent adsorption performance and recyclability. The MnFe2O4/CNTs were more effective than CoFe2O4/CNTs for BZF adsorption. When the initial concentration of BZF was varied from 5 to 40 mg L−1, the maximum adsorption capacity of MnFe2O4/CNTs and CoFe2O4/CNTs increased from 14.8 to 33.4 mg g−1 and 8.1 to 27.8 mg g−1, respectively. Moreover, the Langmuir isotherm model and pseudo-second-order equation could elaborate well the adsorption of BZF on MFe2O4/CNTs. The thermodynamic analysis further revealed that the adsorptions were spontaneous processes. Based on measurements of surface and pore diffusion and the results of adsorption reactions, possible mechanisms were proposed to explain the adsorption process. This research indicates that the MFe2O4/CNTs are potentially applicable for the removal of BZF from aqueous solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...