Production of acetic acid from ethanol over CuCr catalysts via dehydrogenation-(aldehyde–water shift) reaction
Abstract
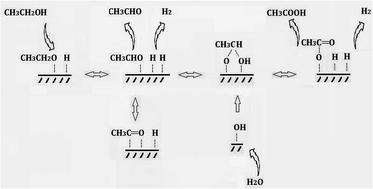
A series of CuCr catalysts were prepared by co-precipitation method and used to produce acetic acid from ethanol via dehydrogenation-(aldehyde–water shift) reaction. The catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis (BET), inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), and temperature programmed reduction (TPR). The effects of copper contents and atmosphere on catalytic performance were investigated. The enhanced catalytic performance can be ascribed to the existence of chromium oxide. A possible mechanism for the production of acetic acid from ethanol without oxidant was also proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...