Synthesis of zinc-based acrylate copolymers and their marine antifouling application†
Abstract
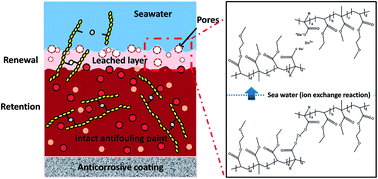
Marine fouling organisms have caused inconvenience to humans for a long time owing to their high vitality and great destructiveness. Self-polishing antifouling coatings are considered to be among the most effective antifouling technologies. In this study, zinc-based acrylate copolymers (ZnPs) were designed and synthesized using a bifunctional zinc acrylate monomer (ZnM) as a new self-polishing monomer, and three acrylate monomers (namely, methyl methacrylate, ethyl acrylate and 2-methoxyethyl acrylate) were used as comonomers. ZnPs that contained the new ZnM were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and gel permeation chromatography. Different antifouling coatings were prepared using the previously mentioned ZnPs as the matrix material, and their erosion properties were investigated using a lab rotor test. A field test of the prepared coatings at various geographical locations showed their excellent antifouling performance as they inhibited the settlement of barnacles in both the South China Sea for 9 months and in the Yellow Sea for at least 15 months. The results of this study highlight that the biocidal ZnP-based coatings are highly promising candidates for marine antifouling applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...