In vitro–in vivo and pharmacokinetic evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticles of furosemide using Gastroplus™
Abstract
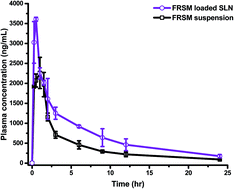
In this work, we conducted pharmacokinetic studies and established the in vitro and in vivo correlation (IVIVC) of furosemide (FRS) loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (FSLN). A bioanalytical method using RP-HPLC was developed and validated to evaluate the pharmacokinetic properties of FSLN and FRS suspension (FSP). The pharmacokinetic parameters were analyzed using various pharmacokinetic compartment models (one, two and three) and non-compartmental analysis. The IVIVC was accomplished using numerical deconvolution (single Weibull and double Weibull), the Wagner-Nelson (one compartment model) and the Loo-Riegelman method (two and three compartment model) via GastroPlus™ software. The method was developed and successfully validated for the quantification of FRS in plasma. An enhancement in Cmax from 2261.7 ng mL−1 (FSP) to 3604.7 ng mL−1 FSLN, and AUC0→24 from 10 130 ng h mL−1 (FSP) to 17 077 ng h mL−1 (FSLN) indicated an enhancement in the oral bioavailability of FRS when given in the form of SLN. In the statistical analysis, the Loo-Riegelman method was found to be the best-fit deconvolution method for establishing the IVIVC of FSLN. As an innovative approach, having more restrictive and conclusive IVIVC, the entire plasma profile of the convoluted and observed was divided into three time phases, (i) 0 → 0.5 h, (ii) 0.5 → 3 h and (iii) 3 → 24 h, and statistically analyzed to demonstrate IVIVC. The study showed that FSLN could be a potential drug carrier for the delivery of FRS with improved bioavailability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...