Synthesis of a poly(amidoxime-hydroxamic acid) cellulose derivative and its application in heavy metal ion removal†
Abstract
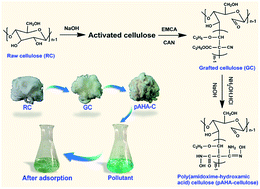
Amidoxime and hydroxamic acid functional groups have comparable chelating ability with synthetic resins, but the synthesis of cellulose fibers bearing amidoxime and hydroxamic acid functional groups using simple and effective strategies have yet to be developed. In this study, a poly(amidoxime-hydroxamic acid) cellulose derivative (pAHA-cellulose) was prepared via free radical polymerization followed by an oximation reaction. A series of microscopic analyses and spectral tests proved that the pAHA-cellulose was covered with uniform amidoxime and hydroxamic acid functional groups. The use of pAHA-cellulose towards heavy metal ion removal was investigated and an uptake equilibrium was achieved within 60 min for Cu2+ and Zn2+, and 120 min for Pb2+ and Cr3+, through a chelation mechanism. The adsorption behavior followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm with Langmuir maximum adsorption capacities of 395.3, 333.3, 268.8 and 216.9 mg g−1 for Cu2+, Pb2+, Cr3+ and Zn2+, respectively. Regeneration of pAHA-cellulose did not significantly influence the adsorption towards metal ions for up to five sequential cycles. Considering the simple and efficient grafting process, excellent adsorbability and prominent renewability, pAHA-cellulose is believed to be a new and feasible candidate for heavy metal ion removal from aqueous solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...