Peptide-binding induced inhibition of chemokine CXCL12†
Abstract
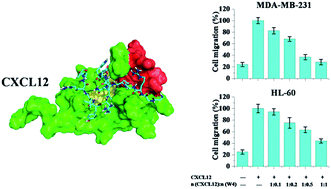
The chemokine CXCL12, and its receptor CXCR4, have been recognized to be involved in various instances of cancer metastasis. The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis has emerged as a potential target for cancer therapy. Here, we demonstrate a designed peptide (W4) targeting CXCL12 with high binding affinity, and describe its significant inhibitory effect on the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis. We show that W4 has comparable binding affinity (KD = 5.7 × 10−8 M) to that of the antibody of CXCL12 (KD = 3.0 × 10−9 M) using the surface plasma resonance (SPR) technique. Upon introduction of W4, the circular dichroism (CD) spectra show that the α-helical structure of CXCL12 gradually transformed into a β-sheet and random coil. These effects lead to the significant inhibitory effects on the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis using the CXCR4-positive breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 and the leukemia cell lines HL-60 and U937 as models. The results show that W4 significantly inhibits CXCL12-induced cell migration of MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, HL-60 and U937 even to 20.0% when the mole ratio is 1 : 1, completely abolishing the effect of CXCL12. These effects may provide evidence of the modulating ligand–receptor interactions of peptides as anti-ligand molecules that differ from the traditional receptor antagonists leading to therapeutic agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...