Ag3PO4/CoFe2O4 magnetic nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization and applications in catalytic reduction of nitrophenols and sunlight-assisted photocatalytic degradation of organic dye pollutants
Abstract
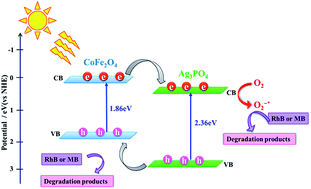
A novel magnetically recyclable Ag3PO4/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite (containing 30 wt%. CoFe2O4) was synthesized by a facile hydrothermal method. The composition and microstructure of the nanocomposite was fully characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), UV-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM)-energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). Thereafter, the catalytic performance of the Ag3PO4/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite was investigated. The Ag3PO4/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite showed high efficiency for the degradation of methylene blue (MB) and Rhodamine B (RhB) dyes under direct sunlight irradiation. The photocatalytic activity of Ag3PO4/CoFe2O4 under sunlight irradiation was almost 1.5 and 4.7 times as high as those of the pure Ag3PO4 and CoFe2O4, respectively. The enhancement of sunlight photocatalytic activity in Ag3PO4/CoFe2O4 should be assigned to the effective separation and transfer of photogenerated charges originating from the well-matched overlapping band-structures. Trapping experiments indicated that superoxide anion (˙O2−) radicals were the main reactive species for dye degradation in the present sonocatalytic system. A proposed mechanism for the enhanced photocatalytic activity is also discussed based on the experimental results. In addition, the catalytic activity of the nanocomposite in the reduction of nitrophenols by using NaBH4 was evaluated. The results showed that Ag3PO4/CoFe2O4 exhibited the best performance in the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) and 2-nitrophenol (2-NP) and revealed 100% conversion into the corresponding amino derivatives within 24–46 min with rate constant equal to 0.0714 min−1 and 0.0329 min−1, respectively. Moreover, due to the existence of the CoFe2O4, the Ag3PO4/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite could be magnetically separated from the reaction mixture and reused without any change in structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...