Nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC)-based novel hydrogels as potential carriers for nepafenac applied after cataract surgery for the treatment of inflammation: design, characterization and in vitro cellular inhibition and uptake studies†
Abstract
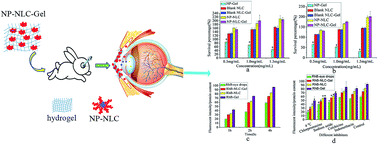
The objective of this study was to design innovative nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) nanoparticle-loaded hydrogels for drug delivery of nepafenac (NP) applied after cataract surgery for the treatment of postoperative inflammation. NP-NLC nanoparticles were prepared with NP, glycerin monostearate, Miglyol, soy lecithin and Cremophor EL using a melt emulsification method. A two-factor five-level central composite design (CCD) was introduced to perform the experiments. A quadratic function was generated to predict and evaluate the independent variables with respect to the dependent variables. An analysis of variance (ANOVA) statistical test was used to assess the optimization. The morphology of the nanoparticles assessed using TEM revealed a nearly spherical shape. The particle size of the nanoparticles was 92.42 ± 3.46 nm. DSC analyses indicated that NP was mostly entrapped in the amorphous state. Rheological studies indicated that the gelation temperature of the hydrogels and the NP-NLC hydrogels (NP-NLC-Gel) are 28.5 °C and 32.0 °C respectively. At 35 °C and pH 7.4, the swelling ratio of the NP-NLC-Gel was 8033%. The results of cytotoxicity studies also suggested that NLC-Gel was biocompatible with no significant cytotoxicity observed in the human corneal epithelial cells (HCECs). Preliminary cellular uptake tests proved an enhanced penetration of nepafenac into HCECs when encapsulated in NLCs. The inhibition study suggested that cell uptake was dependant on energy and the clathrin-mediated pathway. Therefore, these results together suggested that the NP-NLC-Gel prepared in this study could be developed as a preliminarily successful carrier for delivering nepafenac for the treatment of inflammation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...