Near-infrared probes based on fluorinated Si-rhodamine for live cell imaging†
Abstract
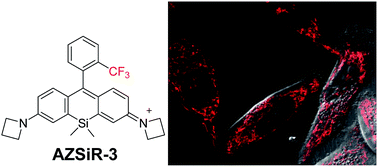
The syntheses and biological applications of three Si-rhodamine probes with substituent groups on the pendant phenyl ring are reported. In solution, these Si-rhodamine probes (AZSiR) show slight aggregation. By introducing a methyl group at the 2-position of the pendant phenyl ring, the AZSiR-2 probe shows almost unchanged absorption and emission peaks, and a three times higher fluorescence quantum yield than that of AZSiR-1. However, the photostability of the AZSiR-2 probe becomes poor. By changing the substituent groups from methyl to trifluoromethyl, the AZSiR-3 probe displays slightly red-shifted absorption and emission peaks, and good photostability. Furthermore, the bulky groups on the phenyl ring of Si-rhodamine prevent nucleophilic attack through steric hindrance, and endow Si-rhodamine probes good chemical stability in nucleophilic systems. These Si-rhodamine probes have excellent live cell permeability and low cytotoxicity. Importantly, the Si-rhodamine probe with trifluoromethyl at the 2-position of the pendant phenyl ring retains high brightness and excellent stability even in a harsh physiological environment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...