Nanoparticle functionalized laser patterned substrate: an innovative route towards low cost biomimetic platforms†
Abstract
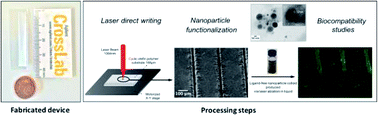
Integration of nanotechnology and advanced manufacturing processes presents an attractive route to produce devices for adaptive biomedical device technologies. However, tailoring biological, physical, and chemical properties often leads to complex processing steps and therefore to high manufacturing cost impeding further scalability. Herein, a novel laser-based approach is introduced to manufacture low cost biocompatible polymer substrates functionalized with ultrapure nanoparticles. Laser direct writing was performed to create micron-sized patterns on 188 μm-thick cyclic olefin polymer (COP) substrates using a picosecond pulsed 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser. The Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids (PLAL) technique was exploited in this work to prepare colloidal solutions of ultrapure nanoparticles to impart bio-functionality onto laser patterned surfaces. Combining the laser patterns and their modification with PLAL-nanoparticles resulted in a functional and biocompatible substrate for biosensing applications. Our in vitro cell viability studies using a model cell line (human skin keratinocyte, HaCaT) suggest that these nanoparticles immobilized on the surfaces function as a biomimetic platform with the ability to interact with different biological entities (e.g. DNA, antibodies etc.).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...