Electronic properties of TiO2-based materials characterized by high Ti3+ self-doping and low recombination rate of electron–hole pairs†
Abstract
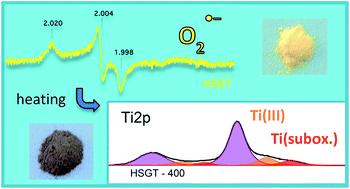
Factors tuning the functional performances of the various TiO2-based materials in the wide range of their possible applications are poorly understood. Here the electronic structure of TiO2-based materials characterized by Ti3+ self-doping, obtained by a sol–gel route wholly performed in air at room temperature, is reported. In the amorphous hybrid TiO2–acetylacetonate (HSGT) material the formation of the Ti(IV)–acac complex makes it photoresponsive to visible light and allows us to obtain by means of a simple annealing in air at 400 °C a very stable black Ti3+ self-doped anatase TiO2 nanomaterial (HSGT-400), characterized by an extraordinary high concentration of Ti atoms with oxidation states lower than IV (about 26%), which absorbs light in the entire visible range. The very high stability of HSGT-400 is mainly related to the process, which does not require the use of harsh conditions nor external reducing agents. The electronic structure of HSGT, owing to the presence of the Ti(IV)–acac complex, allows the stabilization of superoxide anion radicals on its surface for a very long time (months) at room temperature. The extraordinary low recombination rate of electron–hole pairs gives to HSGT unusual catalytic performances at room temperature allowing the complete removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol from water in about one hour without any light irradiation. Our results clearly highlight the connection among the production process of TiO2-based materials, their electronic structure and, finally, their functional behaviour.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...