Synthesis of human hair fiber-impregnated chitosan beads functionalized with citric acid for the adsorption of lysozyme
Abstract
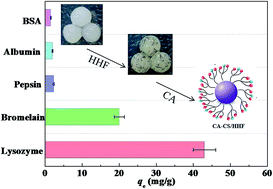
Chitosan materials have been applied widely in protein separation and purification processes, however, pure chitosan materials generally suffer from inadequate mechanical properties and low densities of active adsorption sites, thereby leading to short service lives, limited actual re-usage counts and unexpected re-absorption capacities as adsorbents. Herein, a novel CA-CS/HHF composite was firstly constructed by impregnating human hair fiber into a CS matrix and then functionalized with citric acid. The structures and morphologies of the thus-produced composites were characterized by FTIR and SEM, respectively. A mechanical stability test showed that the impregnation of HHF into the chitosan matrix could effectively enhance the mechanical stability of the CA-CS/HHF beads in comparison with pure chitosan spheres. The adsorption of proteins and a protein mixture revealed that the product could adsorb positively charged proteins, as ascertained by the method of sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The maximum value for LYZ adsorption on the CA-CS/HHF composite was 42.1 mg g−1 with a fast equilibrium time of 3 h. Moreover, the resultant product exhibited good reversibility with respect to lysozyme. This simple and intriguing approach characterized by both environmental conservation and waste recycling strongly extends any future utilization of human hair fiber, and the resultant CA-CS/HHF can potentially be truly applied for the quick and effective adsorption of positively charged lysozyme.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...