Efficient and stable ZrO2/Fe modified hollow-C3N4 for photodegradation of the herbicide MTSM†
Abstract
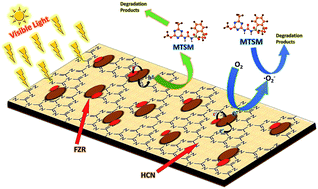
Hollow graphitic carbon nitride (HCN) ZrO2/g-C3N4 hybrid composites (HCN–ZR) and the target catalyst Fe/ZrO2/g-C3N4 (HCN–FZR) were prepared successfully by a solvo-thermal method and evaluated for photo-degradation of organic pollutants, i.e. MO, and herbicides, metsulfuron methyl (MTSM). These materials were characterized by a variety of techniques, including Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, UV-vis spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, HPLC-MS and scanning electron microscopy. The characterization and degradation results showed that FZR particles are well distributed on the surface of HCN to give a photo-catalytically active material. Photodegradation split MTSM completely into a lot of intermediate products, as depicted in the HPLC-MS results. Mooring of FZR on HCN increased the surface-area and light absorption capability of HCN–FZR, due to heterojunction formation between the semiconductors, which retarded electron–hole recombination and enhanced the photo-activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...