Structural changes of poplar wood lignin after supercritical pretreatment using carbon dioxide and ethanol–water as co-solvents†
Abstract
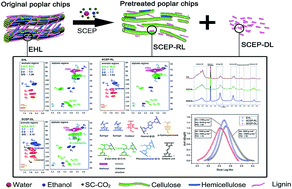
To delineate the structural changes of lignin during supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment with ethanol–water as co-solvents (SCEP), enzymatic hydrolysis lignin (EHL) in original poplar chips, residual lignin in SCEP pretreated residues (SCEP-RL) and lignin dissolved in the SCEP liquors (SCEP-DL) were sequentially isolated and systematically characterized by GPC, quantitative 13C-NMR, 31P-NMR, 2D-HSQC NMR and TGA. After SCEP process, 19.2% of lignin was degraded and dissolved into SCEP liquors, while 4.8% of lignin was still present in the pretreated residues. It was also convinced that parts of the β-O-4 aryl ether linkages were cleaved and some of the stilbene, resinol (β–β) and phenylcoumaran (β-5) units were increased during SCEP process. Furthermore, the contents of free phenolic hydroxyl groups and carboxylic acids in SCEP-RL and SCEP-DL were higher than that of EHL.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Biofuels and biomass for a clean environment


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...