Experimental studies of hydrocarbon separation on zeolites, activated carbons and MOFs for applications in natural gas processing
Abstract
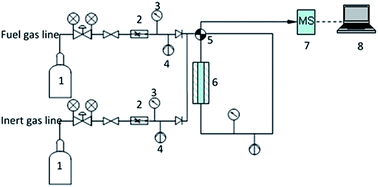
Separation of minor hydrocarbon components in natural gas is necessary prior to liquefaction to avoid operational (plugging of equipment) and product specification issues. While there have been many studies describing adsorption of gases on solid materials there have been relatively few focused on decreasing concentrations of light hydrocarbons in methane in non-equilibrium experimental configurations. In order to best understand the chemistry of competitive adsorption of saturated hydrocarbons for gas processing applications we investigated light hydrocarbon dynamic adsorption properties on 16 solid adsorbents of different structures and chemistries. The best adsorbents, as determined by adsorption capacity, were tested for their ability to separate higher molecular weight hydrocarbons from methane. It is found that for charged frameworks, the induced dipole moment between the adsorbent and adsorbate plays the most important role in adsorption capacity. For uncharged frameworks, pore size plays the critical role in adsorption: micropores are more effective than mesopores. For separation of mixtures of methane, ethane, propane and butane, the kinetics of adsorption must also be considered. Of the materials tested, a carbon derived from coal and activated with steam (carbon #5 (37771)), zeolite KX and zeolite 5A were the best in terms of adsorption and separation capability. These materials show promise for separating light hydrocarbons of similar chemical nature.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...