Controlled exfoliation of monodispersed MoS2 layered nanostructures by a ligand-assisted hydrothermal approach for the realization of ultrafast degradation of an organic pollutant†
Abstract
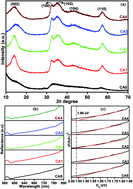
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) layered nanosheets were synthesized by the hydrothermal method. Citric acid was used as an organic ligand to obtain the monodispersed layered MoS2 nanostructures. The effect of citric acid on the formation and functional properties of the layered MoS2 nanostructures was investigated. The X-ray diffraction patterns revealed the formation of a hexagonal crystal structure of MoS2. Significant peak shift was observed for the interaction of citric acid and Mo in the core level spectra of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Citric acid-free hydrothermal growth resulted in the formation of micron-sized MoS2 nanospheres, whereas citric acid-assisted hydrothermal growth resulted in the formation of well dispersed layers of MoS2, confirmed by morphological analysis. However, the highest concentration of citric acid resulted in the formation of aggregated layers. The obtained MoS2 nanostructures were used as photocatalysts to decompose methylene blue (MB) as a model pollutant. The obtained results showed that the MoS2 layered nanosheets could effectively decompose the organic pollutant. The MB absorption peaks completely disappeared after 24 min of irradiation when using the nanosheets synthesized with a citric acid concentration of 0.04 M. The effect of pH on the MoS2 nanosheets was studied, and 96% MB degradation was observed at pH 12 after 2 min of visible-light irradiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...